Faceless Assessment under Section 144B of Income Tax Act: A Comprehensive Legal Framework and Implementation Analysis
Introduction
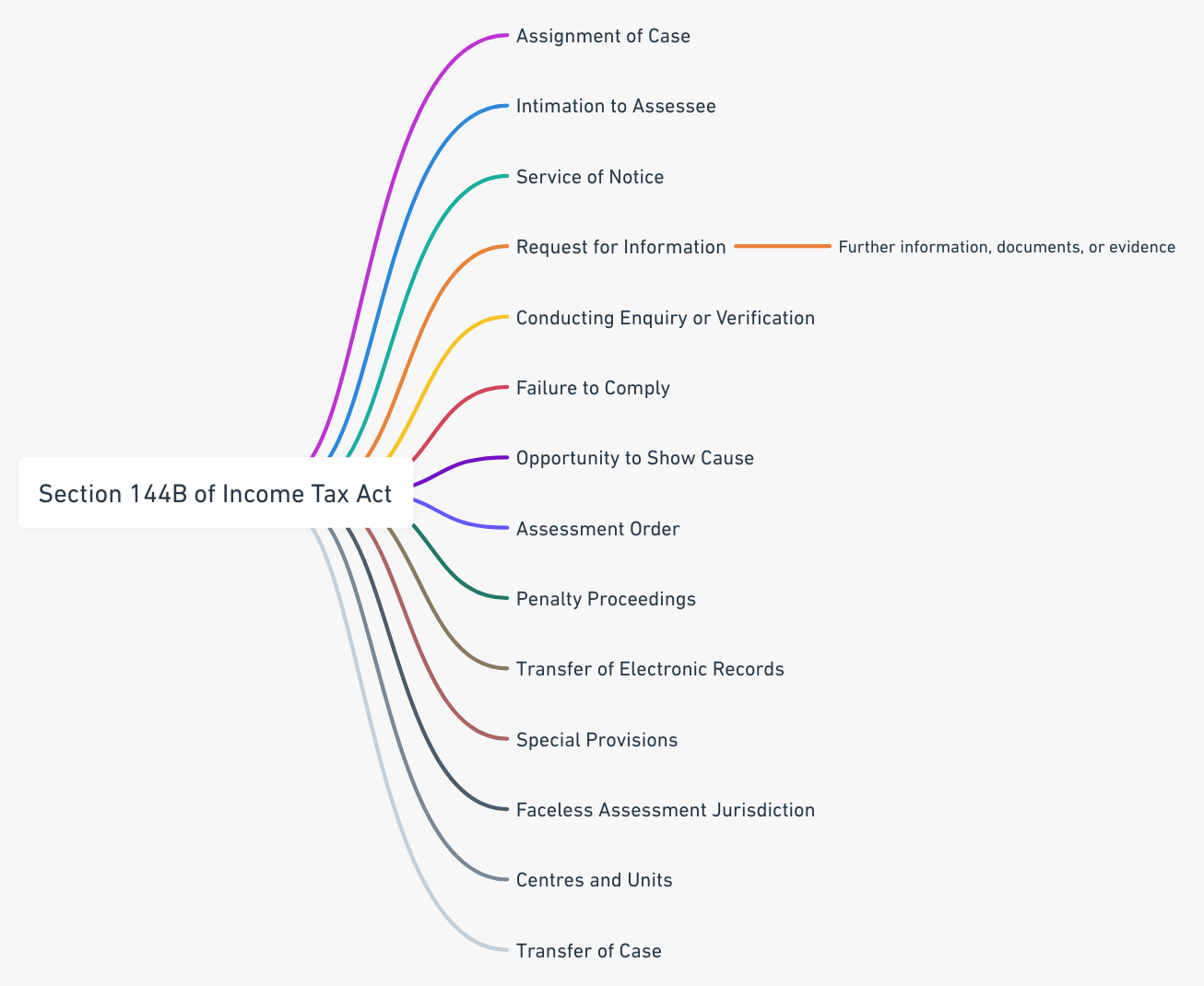
The Indian taxation landscape witnessed a revolutionary transformation with the introduction of the Faceless Assessment Scheme under Section 144B of the Income Tax Act, 1961 [1]. This paradigmatic shift represents the government’s commitment to leveraging technology for creating a more transparent, efficient, and accountable tax administration system. The scheme fundamentally eliminates direct physical interaction between assessing officers and taxpayers, establishing a digital ecosystem where assessments are conducted through virtual means without revealing the personal identities of either party.
The conceptual foundation of faceless assessment emerged from the pressing need to address longstanding issues in the traditional assessment system, including corruption, bias, geographical limitations, and resource inefficiencies. The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) introduced this revolutionary framework through comprehensive notifications, establishing a robust legal structure that ensures procedural fairness while maintaining the integrity of tax collection processes [2].
Legislative Framework and Regulatory Foundation
Constitutional and Statutory Basis
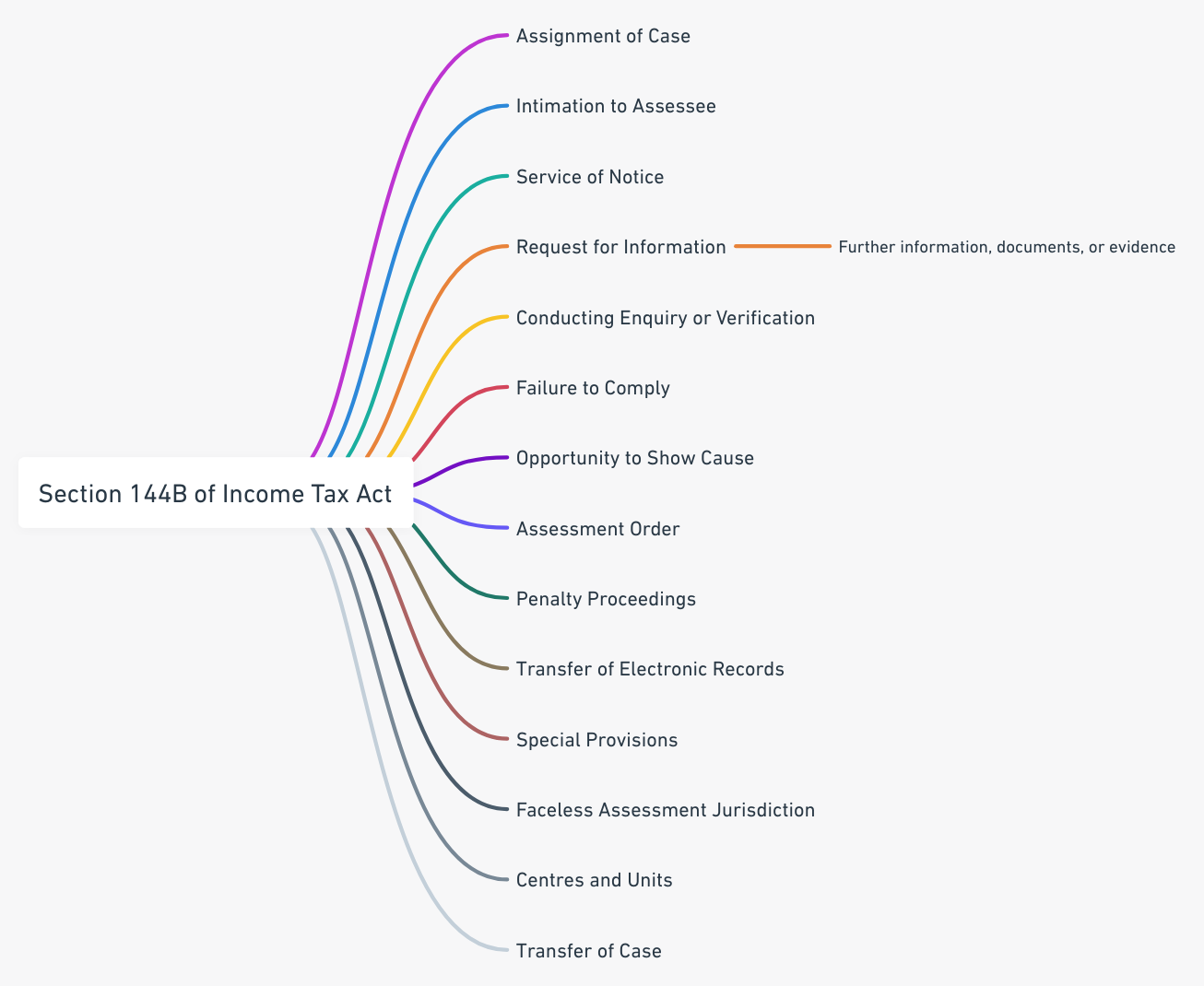
Section 144B was inserted into the Income Tax Act, 1961, through the Finance Act 2020, providing the statutory foundation for conducting faceless assessments. The provision empowers the Central Government to establish schemes for faceless assessment, creating a legal framework that supersedes traditional assessment procedures under specific circumstances [3].
The section reads: “Notwithstanding anything to the contrary contained in section 143 or section 144, where the Central Government considers it necessary or expedient to do so for the purpose of imparting greater efficiency, transparency and accountability in income-tax assessment, the Central Government may, by notification in the Official Gazette, establish a scheme for faceless assessment.”
This legislative mandate establishes the primacy of faceless assessment over conventional methods, demonstrating the government’s strategic intent to modernize tax administration through technological integration and process standardization.
Regulatory Implementation Through CBDT Notifications
The Central Board of Direct Taxes operationalized Section 144B through Notification No. 60/2020 and subsequent amendments, establishing the comprehensive Faceless Assessment Scheme [4]. These notifications delineate the procedural framework, institutional structure, and operational guidelines that govern the entire faceless assessment ecosystem.
The notifications establish clear parameters for case selection, automated allocation systems, and procedural safeguards that ensure compliance with constitutional principles of natural justice while maintaining operational efficiency. The regulatory framework addresses critical aspects including timeline management, documentation requirements, and quality assurance mechanisms.
Institutional Architecture of Faceless Assessment
National Faceless Assessment Centre (NFAC)
The National Faceless Assessment Centre serves as the central coordinating authority and primary interface between taxpayers and the tax administration under the faceless assessment regime. Established as a virtual entity, NFAC operates through sophisticated technological infrastructure that enables seamless case management, communication, and decision-making processes [5].
NFAC functions as the singular point of contact for all faceless assessment proceedings, ensuring standardized communication protocols and maintaining comprehensive case records. The centre coordinates with various specialized units to ensure effective case processing while maintaining complete anonymity of both assessing officers and taxpayers throughout the assessment proceedings.
Assessment Units and Specialized Functions
The faceless assessment architecture incorporates multiple specialized units designed to handle specific aspects of the assessment process. Assessment units are responsible for conducting detailed examination of cases, analyzing financial records, and preparing draft assessment orders based on available evidence and taxpayer responses.
These units operate independently within designated geographical jurisdictions, receiving case assignments through automated allocation systems that prevent any direct correlation between specific officers and particular taxpayers. The specialization ensures that cases are handled by officers with relevant expertise while maintaining the anonymity essential to the faceless assessment concept.
Verification and Technical Units
Verification units play crucial roles in conducting field inquiries, gathering additional evidence, and performing technical analysis when required during assessment proceedings. These units operate under strict confidentiality protocols, ensuring that their findings and recommendations are transmitted through secure channels without compromising the faceless nature of the proceedings.
Technical units provide specialized expertise in complex matters requiring detailed analysis of specific industries, accounting practices, or regulatory compliance issues. Their involvement ensures that assessments maintain technical accuracy while adhering to established legal standards and procedural requirements.
Automated Case Allocation System
Technological Framework and Artificial Intelligence Integration
The automated allocation system represents the technological backbone of the faceless assessment scheme, utilizing advanced algorithms, artificial intelligence, and machine learning capabilities to ensure optimal resource utilization and unbiased case distribution [6]. This system eliminates human intervention in case assignment, preventing any possibility of manipulative practices or preferential treatment.
The allocation system considers multiple parameters including case complexity, officer expertise, workload distribution, and geographical factors while maintaining complete randomness in assignment patterns. The integration of artificial intelligence enables continuous learning and optimization, improving allocation efficiency based on historical performance data and outcome analysis.
Transparency and Accountability Mechanisms
The automated system maintains comprehensive audit trails documenting all allocation decisions, case movements, and timeline adherence. These records ensure complete transparency in case handling while providing accountability mechanisms that can be reviewed for process improvement and compliance verification.
Regular system audits and performance evaluations ensure that the allocation mechanisms remain fair, efficient, and aligned with the scheme’s objectives. The technological framework includes built-in safeguards against system manipulation and unauthorized access, maintaining the integrity of the entire faceless assessment process.
Notice and Communication Procedures
Electronic Service of Notices
The faceless assessment scheme mandates electronic service of all notices, communications, and orders through the National Faceless Assessment Centre. This digital communication framework ensures uniform standards, maintains proper documentation, and eliminates geographical barriers that traditionally affected tax proceedings [7].
Notices issued under Section 143(2) or Section 142(1) through NFAC follow standardized formats and include comprehensive information regarding the nature of inquiries, required documents, and response timelines. The electronic system automatically generates acknowledgment receipts and maintains delivery confirmations, ensuring proper service documentation for legal compliance.
Response Submission and Processing
Taxpayers are required to submit all responses, documents, and representations through designated electronic channels within specified timeframes. The system provides secure upload mechanisms, document verification protocols, and submission confirmations that ensure proper receipt and processing of taxpayer communications.
The centralized response processing system enables efficient document management, automated case updates, and seamless integration with assessment units for timely consideration of taxpayer submissions. All responses are time-stamped and digitally archived, creating permanent records that can be referenced throughout the assessment proceedings.
Assessment Process and Procedural Safeguards
Draft Assessment Order Procedures
The faceless assessment scheme incorporates mandatory draft assessment order procedures that ensure taxpayers receive adequate opportunity to respond to proposed adjustments before finalization of assessments. This procedural safeguard addresses constitutional requirements of natural justice while maintaining the efficiency of faceless proceedings [8].
Draft orders must clearly articulate the basis for proposed adjustments, cite relevant legal provisions, and provide reasonable timeframes for taxpayer responses. The system ensures that all draft orders are reviewed for legal compliance and factual accuracy before transmission to taxpayers through NFAC.
Personal Hearing Provisions and Virtual Proceedings
Despite the faceless nature of assessments, the scheme provides for personal hearings through video conferencing facilities when requested by taxpayers or deemed necessary by assessing authorities. These virtual hearings maintain the anonymity of proceedings while ensuring that taxpayers receive adequate opportunities to present their cases [9].
The video conferencing infrastructure includes secure authentication mechanisms, recording capabilities, and transcription services that ensure proper documentation of hearing proceedings. All participants remain anonymous through technological measures that prevent identification while enabling effective communication and case presentation.
Judicial Interpretation and Case Law Development
Constitutional Validity and Natural Justice Compliance
Various High Courts have examined the constitutional validity of faceless assessment procedures, generally upholding the scheme while emphasizing strict adherence to procedural requirements and natural justice principles. In several landmark judgments, courts have recognized the scheme’s potential for enhancing transparency while insisting on proper implementation of procedural safeguards.
The Madras High Court in a significant ruling emphasized that faceless assessment does not diminish the requirement for providing adequate opportunities to taxpayers, including reasonable time for responses and access to personal hearings when requested. The court established that minimum 21 days should be provided for responses to assessment notices, ensuring meaningful opportunity for case presentation.
Procedural Compliance and Validity Requirements
Courts have consistently held that strict compliance with prescribed procedures under Section 144B is essential for the validity of assessment orders. Cases where proper notices were not issued, adequate time was not provided, or procedural requirements were not followed have resulted in assessment orders being quashed by various High Courts.
The Delhi High Court and other jurisdictions have emphasized that the combination of show cause notices and draft assessment orders into single documents violates prescribed procedures and renders such orders invalid. These judicial pronouncements have reinforced the importance of following established protocols within the faceless assessment framework.
Challenges and Practical Implementation Issues
Technical Infrastructure and Digital Divide
The implementation of faceless assessment has encountered various technical challenges related to system reliability, user interface design, and digital accessibility. Many taxpayers, particularly in rural areas and among smaller businesses, face difficulties in adapting to completely digital processes, creating potential compliance barriers.
System downtime, server capacity limitations, and integration issues between different technological platforms have occasionally disrupted assessment proceedings, requiring development of contingency measures and technical support mechanisms. The income tax department has invested significantly in infrastructure upgrades and user training programs to address these challenges.
Procedural Adaptation and Training Requirements
The transition from traditional assessment methods to faceless procedures has required extensive training for both tax officers and taxpayers. Understanding new communication protocols, digital documentation requirements, and virtual hearing procedures has necessitated comprehensive capacity building initiatives.
Tax practitioners and professional advisors have needed to adapt their practice methodologies to effectively represent clients in faceless proceedings, developing expertise in digital case presentation and virtual advocacy techniques. Professional bodies have conducted specialized training programs to enhance practitioner capabilities in faceless assessment environments.
Quality Assurance and Review Mechanisms
Multi-Tier Review Process
The faceless assessment scheme incorporates multi-tier review mechanisms that ensure quality control and legal compliance throughout assessment proceedings. These review processes involve independent examination of assessment orders by specialized review units before finalization and transmission to taxpayers.
Review units examine cases for factual accuracy, legal compliance, and procedural adherence, providing additional quality assurance layers that enhance the reliability of assessment outcomes. The review process includes both automated system checks and manual verification by experienced officers to ensure comprehensive quality control.
Feedback and Continuous Improvement
The scheme includes mechanisms for collecting feedback from stakeholders, analyzing system performance, and implementing continuous improvements based on operational experience. Regular evaluation of case processing times, quality metrics, and taxpayer satisfaction levels inform system enhancements and procedural refinements.
Performance analytics and outcome analysis enable identification of process bottlenecks, system inefficiencies, and areas requiring additional training or resource allocation. This data-driven approach supports ongoing optimization of the faceless assessment framework.
Comparative Analysis with Traditional Assessment Methods
Efficiency and Resource Optimization
Faceless assessment has demonstrated significant improvements in processing efficiency, resource utilization, and case completion timelines compared to traditional methods. The elimination of geographical constraints enables optimal utilization of specialized expertise across different jurisdictions, enhancing overall system productivity.
Standardized procedures and automated workflows have reduced processing delays and improved consistency in assessment outcomes. The system’s ability to handle multiple cases simultaneously through parallel processing has increased overall capacity and reduced assessment backlogs.
Transparency and Corruption Prevention
The faceless system has effectively eliminated opportunities for direct corruption and undue influence that occasionally occurred in traditional face-to-face assessments. The anonymity of proceedings and automated case allocation prevent any possibility of personal relationships affecting assessment outcomes.
Comprehensive digital documentation and audit trails provide transparency that was often lacking in traditional systems, enabling better monitoring and accountability. The standardized communication protocols ensure that all interactions are properly recorded and can be reviewed for compliance verification.
Future Developments and Technology Integration
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Enhancement
Ongoing developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies promise further enhancements to the faceless assessment system. Advanced analytics capabilities will enable better case prioritization, risk assessment, and resource allocation based on sophisticated data analysis.
Predictive modeling and pattern recognition technologies will support early identification of potential compliance issues and enable proactive intervention strategies. Natural language processing capabilities will enhance document analysis and automated case processing efficiency.
Integration with Other Digital Initiatives
The faceless assessment scheme is being integrated with other digital taxation initiatives including faceless appeals, faceless penalty proceedings, and comprehensive taxpayer service portals. This integrated approach aims to create a seamless digital ecosystem for all tax-related interactions.
Future developments will likely include enhanced data analytics, blockchain-based verification systems, and advanced cybersecurity measures to further strengthen the digital taxation infrastructure. These technological advancements will continue improving system reliability, security, and user experience.
Conclusion
The Faceless Assessment Procedure under Section 144B of the Income Tax Act represents a transformative achievement in Indian tax administration, successfully combining technological innovation with established legal principles to create a more efficient, transparent, and accountable assessment system. The scheme has demonstrated the government’s commitment to modernizing tax procedures while maintaining essential procedural safeguards and constitutional compliance.
Despite initial implementation challenges and the need for continuous system improvements, the faceless assessment framework has proven effective in reducing corruption, improving efficiency, and providing standardized treatment to taxpayers across different geographical regions. The judicial endorsement of the scheme, coupled with positive feedback from stakeholders, validates the conceptual foundation and practical implementation of this digital transformation initiative.
As the system continues evolving through technological enhancements and procedural refinements, faceless assessment is poised to become the primary method for conducting tax assessments in India, setting precedents for similar digital governance initiatives in other administrative domains. The success of this scheme demonstrates the potential for technology to enhance public administration while preserving essential principles of fairness, transparency, and accountability.
References
[1] Income Tax Act, 1961, Section 144B – Faceless Assessment. Available at: https://www.taxmanagementindia.com/visitor/detail_act.asp?ID=3299
[2] Central Board of Direct Taxes. (2020). Notification No. 60/2020 – Faceless Assessment Scheme. Available at: https://incometaxindia.gov.in/Pages/faceless-scheme.aspx
[3] ClearTax. (2019). Faceless Assessment Scheme Under Section 144B of Income Tax Act. Available at: https://cleartax.in/s/e-assessment-scheme-2019
[4] TaxGuru. (2020). Faceless Assessment Scheme – Road to transparent taxation. Available at: https://taxguru.in/income-tax/faceless-assessment-scheme-road-transparent-taxation.html
[5] IndiaFilings. (2024). Section 144B of Income Tax Act: Faceless Assessment. Available at: https://www.indiafilings.com/learn/section-144b-of-income-tax-act/
[6] TaxBuddy. (2024). Faceless Assessment: A New Era in Income Tax Proceedings. Available at: https://www.taxbuddy.com/blog/faceless-assessment-scheme
[7] Lexology. (2022). Faceless Assessment Scheme under the Income Tax Act, 1961. Available at: https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=229dd89f-da4f-4564-8bce-43712e5c58b1
[8] Tax Management India. (2021). Validity of order u/s 144B – Faceless assessment – violation of principles of natural justice. Available at: https://www.taxmanagementindia.com/web/tmi_highlights_details.asp?id=60843
[9] Tax Management India. (2025). VALIDITY OF ASSESSENT PASSED UNDER SECTION 144B OF THE INCOME TAX ACT, 1961. Available at: https://www.taxmanagementindia.com/visitor/detail_article.asp?ArticleID=11990
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp