Faceless Assessment Procedure under Section 144B of Income Tax Act: Legal Framework and Operational Units
Introduction
The introduction of Section 144B in the Income Tax Act, 1961, through the Taxation and Other Laws (Relaxation and Amendment of Certain Provisions) Act, 2020, represents a watershed moment in India’s tax administration history [1]. This revolutionary provision, which came into effect from April 1, 2021, fundamentally transformed the traditional assessment methodology by establishing a completely digital, faceless assessment procedure that eliminates physical interaction between taxpayers and tax authorities.
The legislative intent behind Section 144B was crystallized through the government’s “Transparent Taxation – Honouring the Honest” platform launched by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on August 13, 2020 [2]. This initiative aimed to address long-standing issues in tax administration including corruption, arbitrary demands, and lack of transparency that had plagued the conventional assessment system for decades.
The faceless assessment mechanism operates on the fundamental principle of eliminating human interface while maintaining procedural fairness and natural justice. This digital transformation represents not merely a technological upgrade but a complete reimagining of how tax assessments should be conducted in a modern democratic society.

Centre and Units under Faceless Assessment Procedure, Section 144B of Income Tax Act
Legislative Framework and Statutory Authority
Constitutional and Legal Foundation
Section 144B derives its authority from the constitutional framework that empowers Parliament to enact laws relating to taxation under Entry 82 of List I of the Seventh Schedule. The provision operates under the overriding principle established through its non-obstante clause, which states that notwithstanding anything contrary contained in any other provisions of the Income Tax Act, assessments under sub-section (3) of section 143 or under section 144 shall be conducted in a faceless manner [3].
The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT), established under section 3 of the Central Boards of Revenue Act, 1963, serves as the primary regulatory authority for implementing and overseeing the faceless assessment scheme. The CBDT’s powers under section 119 of the Income Tax Act, 1961, provide the necessary administrative framework for operationalizing the faceless assessment procedure through various notifications and circulars.
Regulatory Notifications and Implementation
The operationalization of Section 144B required extensive regulatory support through multiple CBDT notifications. The establishment of the National Faceless Assessment Centre (NaFAC) was formalized through Office Order dated March 31, 2021, which designated Delhi as the headquarters for this centralized facility [4]. This notification specifically outlined the administrative structure, staffing requirements, and jurisdictional boundaries for the faceless assessment system.
CBDT Notification No. 65/2020 dated August 13, 2020, played a crucial role in designating 4,195 Income Tax Authorities across various Regional e-Assessment Centres to exercise concurrent powers as Assessing Officers for facilitating faceless assessment proceedings [5]. This massive administrative restructuring ensured adequate human resources were available to handle the transition from conventional to faceless assessments across the country.
The scope and applicability of the faceless assessment scheme have been further refined through various subsequent notifications. Notable among these is the CBDT order dated September 7, 2021, which specified certain exceptions to the mandatory application of faceless assessment procedure, including cases assigned to Central Charges and International Taxation units, as well as cases where technical constraints prevented the creation of electronic records [6].
Operational Framework: Centres and Units
National Faceless Assessment Centre (NaFAC)
The National Faceless Assessment Centre represents the cornerstone of the entire faceless assessment ecosystem. Established under sub-section (3) of Section 144B, NaFAC functions as the central command and control facility that orchestrates all faceless assessment activities across the country. Located in Delhi, NaFAC serves as the single point of contact between taxpayers and the income tax department, ensuring standardized procedures and consistent application of tax laws.
NaFAC’s primary responsibilities encompass case allocation through automated systems, coordination between various specialized units, management of electronic communications, and maintenance of digital records. The centre operates on advanced technological infrastructure incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to ensure optimal resource utilization and unbiased case distribution.
The administrative structure of NaFAC includes a Principal Chief Commissioner of Income Tax who heads the centre, supported by various ranks of officers, including Additional Commissioners, Joint Commissioners, Deputy Commissioners, Assistant Commissioners, and Income Tax Officers. This hierarchical structure ensures proper supervision and accountability in the faceless assessment procedure.
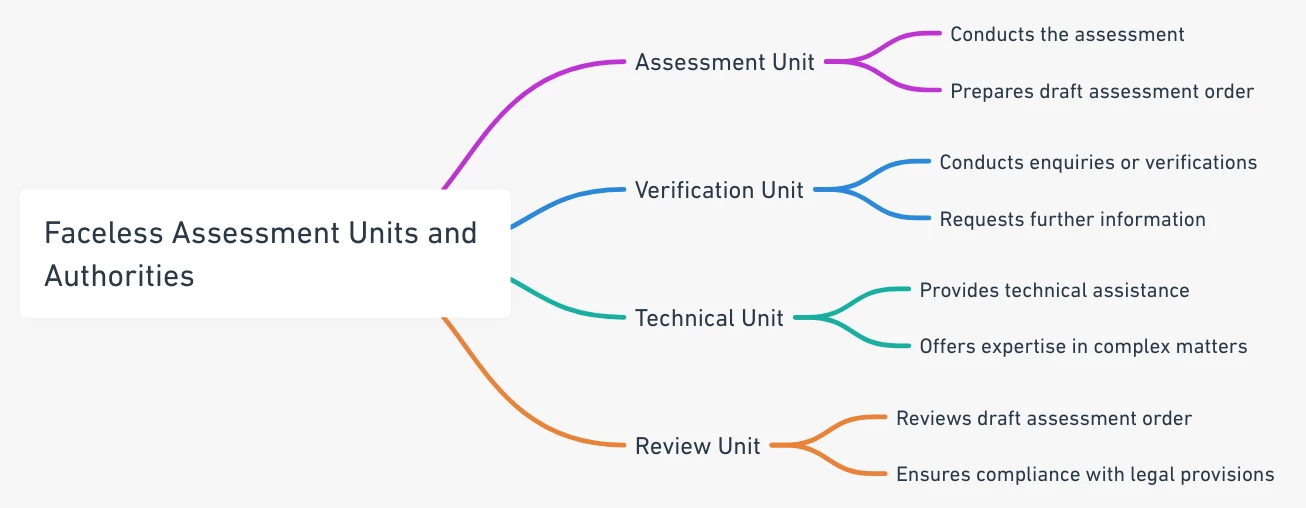
Assessment Units: Core Operational Component
Assessment Units constitute the primary operational component of the faceless assessment procedure, responsible for conducting actual assessments, reassessments, and recomputations under the relevant provisions of the Income Tax Act. These units operate under the administrative control of NaFAC and are staffed by qualified Assessing Officers who possess the requisite technical expertise and legal knowledge.
The functional mandate of Assessment Units extends beyond mere computation of tax liability. These units are empowered to identify material points and issues relevant to liability determination, analyze submitted documents and evidence, seek additional information from taxpayers or third parties, and prepare detailed assessment proposals. The decision-making process within Assessment Units follows structured protocols that ensure consistency and fairness in assessment outcomes.
Assessment Units operate through an automated case allocation system that randomly assigns cases to prevent any possibility of bias or external influence. This technological intervention ensures that neither the taxpayer nor the Assessing Officer knows in advance about the assignment, thereby maintaining the integrity of the assessment process. The units are required to maintain detailed electronic records of all proceedings, which can be accessed for review and audit purposes.
The authority structure within Assessment Units mirrors the traditional assessment hierarchy, with powers distributed among officers of different ranks based on the complexity and value of cases. This ensures that senior officers handle high-value or complex assessments while routine cases are processed by junior officers, optimizing resource utilization and processing efficiency.
Verification Units: Ensuring Accuracy and Compliance
Verification Units serve as specialized entities within the faceless assessment framework, specifically designed to conduct detailed enquiries, cross-verifications, and fact-finding exercises. These units operate independently of Assessment Units to ensure objectivity and thoroughness in verification processes.
The functional scope of Verification Units encompasses examination of books of account, recording of statements from taxpayers and third parties, cross-verification of information with external databases, physical verification of assets where necessary, and validation of claims made by taxpayers. These units employ both technological tools and traditional investigation methods to ensure comprehensive verification.
Verification Units are staffed by experienced officers who possess specialized skills in financial analysis, forensic accounting, and investigation techniques. The units operate under strict timelines to ensure that verification activities do not unduly delay the assessment process. All verification activities are conducted through electronic modes, with personal interactions limited to video conferencing facilities.
The automated allocation system ensures that verification requests from Assessment Units are randomly assigned to Verification Units located in different geographical regions, preventing any possibility of collusion or bias. This geographical separation between Assessment and Verification Units adds an additional layer of security to the entire process.
Technical Units: Specialized Expertise and Advisory Services
Technical Units represent the knowledge backbone of the faceless assessment system, providing specialized technical assistance on complex matters that require expert knowledge. These units are staffed by professionals with expertise in various technical domains including legal interpretation, accounting standards, forensic analysis, information technology, valuation, transfer pricing, and data analytics.
The establishment of Technical Units addresses a critical gap in the traditional assessment system where Assessing Officers often lacked specialized knowledge to handle complex technical issues. By centralizing technical expertise, the faceless assessment system ensures that all assessments benefit from the highest level of technical competence available within the income tax department.
Technical Units operate on a consultation model, where Assessment Units can seek technical assistance on specific issues by submitting detailed queries through NaFAC. The automated allocation system ensures that technical queries are assigned to units with relevant expertise, while maintaining anonymity to prevent any external influence.
The scope of technical assistance provided by these units is expansive, covering areas such as determination of arm’s length price in transfer pricing cases, valuation of complex financial instruments, interpretation of intricate legal provisions, analysis of sophisticated business models, and application of international tax treaties. This specialized support significantly enhances the quality and consistency of assessment decisions across the country.
Review Units: Quality Assurance and Compliance Monitoring
Review Units function as the quality assurance mechanism within the faceless assessment framework, ensuring that all assessment proposals meet the required standards of legal compliance, factual accuracy, and procedural adherence. These units operate independently of Assessment Units to provide objective review and feedback on draft assessment orders.
The review process conducted by these units involves multiple layers of scrutiny including verification of factual accuracy, examination of legal principles applied, assessment of evidence considered, evaluation of judicial precedents cited, and checking for arithmetical accuracy. This multi-dimensional review process ensures that final assessment orders are robust and legally sustainable.
Review Units are staffed by senior officers with extensive experience in tax law and assessment procedures. These officers bring their expertise to bear on complex cases, providing valuable insights and recommendations that enhance the quality of final assessment orders. The review process operates under strict timelines to ensure that quality assurance does not compromise processing efficiency.
The independence of Review Units from the assessment process ensures that their evaluation is objective and unbiased. The units provide detailed feedback to Assessment Units, highlighting any deficiencies or areas requiring additional consideration. This feedback mechanism creates a continuous improvement cycle that enhances the overall quality of the faceless assessment system.
Communication Framework and Electronic Procedures
Electronic Communication Protocol
The faceless assessment system operates entirely through electronic communication channels, eliminating all forms of physical interaction between taxpayers and tax authorities. Section 144B(5) specifically mandates that all communications among Assessment Units, Review Units, Verification Units, Technical Units, taxpayers, and other persons shall be conducted exclusively through NaFAC.
The electronic communication framework operates through secure digital platforms that ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of all communications. Taxpayers receive notices and communications through their registered accounts on the income tax portal, registered email addresses, or mobile applications approved by the income tax department. This multi-channel approach ensures that taxpayers receive timely and reliable communication regarding their assessment proceedings.
The system incorporates robust security measures including digital signatures, encryption, and audit trails to prevent unauthorized access or manipulation of communications. All electronic communications are time-stamped and digitally preserved to maintain a complete record of interactions throughout the faceless assessment Procedure.
Notice and Response Procedures
The faceless assessment Procedure begins with the service of notice under section 143(2) by NaFAC to taxpayers whose cases have been selected for scrutiny. This notice is served electronically through the designated communication channels and provides taxpayers with fifteen days to file their response [7]. The notice clearly outlines the specific issues under scrutiny and the documents or information required from the taxpayer.
Taxpayers are required to submit their responses electronically through the income tax portal, which provides a user-friendly interface for uploading documents, submitting explanations, and tracking the status of their assessment proceedings. The system automatically generates acknowledgments for all submissions, providing taxpayers with confirmation of receipt and processing.
The electronic response mechanism allows taxpayers to submit comprehensive explanations supported by relevant documents and evidence. The system accommodates various file formats and provides adequate storage capacity to handle complex submissions. Taxpayers can also request additional time for compliance if circumstances warrant such extension.
Personal Hearing Through Video Conferencing
While the faceless assessment system eliminates physical interaction, it recognizes the importance of personal hearings in ensuring natural justice and fair assessment procedures. Section 144B(7) provides that where modifications prejudicial to the taxpayer are proposed in the draft assessment order, the taxpayer may request a personal hearing [8].
Personal hearings under the faceless assessment system are conducted exclusively through video conferencing or video telephony facilities established by CBDT at designated locations. This technological solution ensures that taxpayers can present their case effectively while maintaining the faceless character of the faceless assessment Procedure.
The video conferencing infrastructure is designed to provide high-quality audio and video communication, enabling meaningful interaction between taxpayers and tax authorities. The system incorporates features such as document sharing, screen sharing, and recording capabilities to ensure that hearings are conducted efficiently and comprehensively documented.
CBDT has established video conferencing facilities at strategic locations across the country to ensure accessibility for taxpayers. The scheduling and conduct of video conferencing hearings follow structured protocols that ensure fairness, transparency, and proper documentation of proceedings.
Judicial Interpretation and Case Law Development
Gujarat High Court Precedents on Procedural Compliance
The judicial interpretation of Section 144B has been shaped significantly by various High Court decisions, particularly from the Gujarat High Court, which has emerged as a key forum for adjudicating disputes related to faceless assessment procedure. These judicial pronouncements have established important precedents regarding procedural compliance and natural justice requirements under the faceless assessment framework.
In the landmark case of Map Refoils India Ltd. v. National Faceless E-Assessment Centre, the Gujarat High Court quashed an assessment order worth Rs. 101 crores on the grounds of violation of natural justice principles [9]. The court held that the mandatory procedure under Section 144B, including the issuance of a show-cause notice along with the draft assessment order, must be strictly followed. The court emphasized that any deviation from the prescribed procedure would render the assessment order invalid and legally unsustainable.
The case of Gandhi Realty (India) Private Limited v. Assistant/Joint/Deputy Commissioner of Income Tax further reinforced the requirement for strict compliance with Section 144B procedures. The Gujarat High Court observed that the failure to serve a draft assessment order as required under the statutory provisions constituted not only a breach of natural justice principles but also a complete disregard of statutory requirements, warranting judicial intervention.
In Shree Ganesh Intermediary Private Limited v. National Faceless Assessment Centre, Delhi, the Gujarat High Court quashed the faceless assessment order where the taxpayer was given only one day to respond to notices, finding that such inadequate time violated the principles of natural justice and procedural fairness [10]. The court established that reasonable time must be provided to taxpayers to prepare and submit meaningful responses.
Natural Justice and Procedural Fairness Requirements
The judicial interpretation of Section 144B has consistently emphasized that the faceless nature of assessments does not eliminate the requirement for adherence to natural justice principles. Courts have held that the electronic mode of communication and the absence of physical interaction do not compromise the fundamental right of taxpayers to be heard before adverse decisions are made against them.
The principle of “audi alteram partem” (hear the other side) has been recognized as an integral component of the faceless assessment procedure. Courts have consistently held that taxpayers must be provided adequate opportunity to present their case, submit evidence, and respond to allegations before final assessment orders are passed.
The requirement for service of draft assessment orders has been interpreted as a mandatory procedural safeguard that ensures taxpayers are aware of proposed additions or disallowances and have an opportunity to contest them. Courts have held that the failure to serve draft assessment orders renders the final assessment order a nullity under Section 144B(9).
Judicial decisions have also established guidelines regarding the adequacy of time provided to taxpayers for responding to notices and draft assessment orders. Courts have generally held that extremely short deadlines, particularly those providing less than 12 hours for response, violate natural justice principles and render the assessment proceedings invalid.
Nullity Provisions Under Section 144B(9)
Section 144B(9) contains a critical nullity provision that renders any assessment order passed without following the prescribed faceless assessment procedure as invalid and non-existent in law. This provision has been invoked by various High Courts to quash assessment orders that failed to comply with mandatory procedural requirements.
The nullity provision serves as a powerful judicial tool for ensuring compliance with faceless assessment procedures. Courts have interpreted this provision broadly to encompass all aspects of procedural non-compliance, including failure to serve proper notices, inadequate time for response, non-service of draft assessment orders, and denial of personal hearing opportunities.
The automatic nullity consequence under Section 144B(9) distinguishes procedural violations in faceless assessments from those in conventional assessments, where courts typically have discretion in determining the consequences of procedural lapses. This strict approach reflects the legislative intent to ensure rigorous compliance with faceless assessment procedure.
Regulatory Oversight and Administrative Structure
CBDT’s Administrative Powers and Responsibilities
The Central Board of Direct Taxes exercises extensive administrative powers under Section 144B to establish, maintain, and supervise the faceless assessment infrastructure. These powers include the authority to set up various centres and units, specify their jurisdictions, lay down operational procedures, and monitor compliance with prescribed standards.
CBDT’s regulatory oversight extends to the establishment of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for different units within the faceless assessment system. These SOPs provide detailed guidance on case handling, communication protocols, time limits, and quality standards that must be maintained by all units. The SOPs are periodically reviewed and updated to incorporate lessons learned from operational experience and judicial pronouncements.
The Board’s administrative responsibilities also encompass the technological infrastructure required for faceless assessments. This includes the development and maintenance of secure communication platforms, automated allocation systems, digital document management systems, and video conferencing facilities. CBDT ensures that the technological infrastructure meets the highest standards of security, reliability, and user-friendliness.
CBDT’s oversight function includes monitoring the performance of various centres and units, conducting regular audits of procedures and outcomes, and implementing corrective measures where necessary. This continuous monitoring ensures that the faceless assessment system operates efficiently and effectively while maintaining the highest standards of integrity and fairness.
Standard Operating Procedures and Quality Control
The implementation of Section 144B has been supported by detailed Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) issued by CBDT for Assessment Units, Verification Units, Technical Units, and Review Units. These SOPs, issued under Section 144B(6)(xi), provide operational guidelines that ensure consistency and quality in faceless assessment proceedings across the country.
The SOPs for Assessment Units outline the procedures for case allocation, document analysis, preparation of assessment proposals, and coordination with other units. These procedures ensure that assessments are conducted systematically and thoroughly, with adequate documentation of decision-making processes and rationale.
Verification Unit SOPs provide detailed guidelines for conducting enquiries, cross-verifications, and fact-finding exercises. These procedures ensure that verification activities are conducted efficiently and effectively while maintaining the integrity and objectivity of the investigation process.
Technical Unit SOPs outline the procedures for providing specialized technical assistance, including the format for technical queries, response timelines, and quality standards for technical advice. These procedures ensure that technical assistance is provided promptly and accurately to support the assessment process.
Review Unit SOPs establish the framework for quality assurance, including the criteria for review, feedback mechanisms, and standards for final assessment orders. These procedures ensure that all assessment orders meet the required standards of legal compliance and factual accuracy before finalization.
Technological Infrastructure and Digital Innovation
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
The faceless assessment system represents one of the most sophisticated applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies in tax administration globally. The automated case allocation system utilizes advanced algorithms to ensure random, unbiased distribution of cases among various units while optimizing resource utilization and workload distribution.
Machine learning algorithms are employed to analyze patterns in taxpayer behavior, identify potential areas of non-compliance, and flag cases requiring detailed scrutiny. These technological tools enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the assessment process while reducing the scope for human bias and error.
The AI-powered system continuously learns from assessment outcomes and judicial decisions to refine its selection criteria and improve the quality of case identification. This adaptive learning capability ensures that the system becomes more accurate and effective over time.
Data analytics tools are integrated into the faceless assessment system to provide comprehensive insights into taxpayer profiles, industry trends, and compliance patterns. These analytical capabilities enable more informed decision-making and targeted enforcement actions.
Security and Data Protection Measures
The faceless assessment system incorporates robust security measures to protect sensitive taxpayer information and maintain the integrity of assessment proceedings. Multi-layered security protocols include encryption of all communications, secure authentication mechanisms, and comprehensive audit trails for all system activities.
Digital signatures and time-stamping technologies ensure the authenticity and integrity of all electronic documents and communications. These technological safeguards provide legal certainty regarding the validity and admissibility of electronic records in judicial proceedings.
The system incorporates advanced access controls that ensure only authorized personnel can access relevant case information. Role-based access permissions prevent unauthorized disclosure of confidential information while enabling necessary coordination between different units.
Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments ensure that the technological infrastructure remains secure against evolving cyber threats. Continuous monitoring and threat detection systems provide real-time protection against security breaches and unauthorized access attempts.
Impact on Tax Administration and Compliance
Efficiency and Resource Optimization
The implementation of Section 144B has resulted in significant improvements in the efficiency of tax administration in India. The automated case allocation system has eliminated geographical constraints, enabling optimal utilization of assessment capacity across the country. Cases can now be assigned to any Assessment Unit regardless of location, ensuring that workload is distributed efficiently based on available capacity rather than geographical proximity.
The standardization of procedures and quality control mechanisms has reduced processing times and improved the consistency of assessment outcomes. The electronic communication system has eliminated delays associated with postal communications and physical movement of files, significantly accelerating the assessment process.
The specialization of functions through different types of units has enhanced the quality of assessments while reducing the burden on individual officers. Complex technical issues can now be referred to specialized Technical Units, ensuring that assessments benefit from the highest level of expertise available within the system.
Transparency and Accountability Enhancements
The faceless assessment system has introduced unprecedented levels of transparency and accountability in tax administration. The elimination of physical interaction has removed opportunities for corruption and undue influence, creating a more equitable environment for all taxpayers.
The digital nature of all communications and proceedings creates comprehensive audit trails that can be reviewed and analyzed for quality assurance and compliance monitoring. This enhanced transparency has increased public confidence in the tax administration system and improved voluntary compliance rates.
The automated allocation system ensures that cases are distributed fairly and randomly, eliminating any possibility of favoritism or discrimination. This objectivity in case allocation has created a more level playing field for all taxpayers, regardless of their size or influence.
Challenges and Areas for Improvement
While the faceless assessment system has achieved significant success, certain challenges have emerged during implementation that require continued attention and improvement. Technical glitches and system downtime have occasionally disrupted proceedings, highlighting the need for robust backup systems and technical support infrastructure.
The learning curve associated with new procedures has required extensive training and capacity building for both tax officials and taxpayers. Continued investment in training and support systems is necessary to ensure optimal utilization of the faceless assessment framework.
Some complex cases may require more nuanced handling that is difficult to achieve through purely electronic means. The system continues to evolve to address these challenges while maintaining the core principles of faceless assessment.
Conclusion
Section 144B of the Income Tax Act represents a transformative leap in tax administration that has fundamentally altered the landscape of income tax assessments in India. The establishment of specialized units including Assessment Units, Verification Units, Technical Units, and Review Units has created a sophisticated ecosystem that ensures thorough, fair, and efficient assessment proceedings while maintaining the highest standards of procedural compliance and natural justice.
The legislative framework established through Section 144B, supported by extensive regulatory guidance from CBDT and refined through judicial interpretation, has created a robust foundation for faceless tax administration. The integration of advanced technologies including artificial intelligence, machine learning, and secure digital communication platforms has positioned India as a global leader in digital tax administration.
The judicial interpretation of Section 144B, particularly through Gujarat High Court decisions, has established clear parameters for procedural compliance and reinforced the importance of natural justice principles even in faceless proceedings. These judicial precedents provide valuable guidance for both tax authorities and taxpayers in navigating the faceless assessment framework.
The success of the faceless assessment system lies not merely in its technological sophistication but in its ability to balance efficiency with fairness, transparency with security, and innovation with legal compliance. As the system continues to evolve and mature, it will undoubtedly serve as a model for tax administrations worldwide seeking to modernize their assessment procedures while maintaining the highest standards of procedural fairness and taxpayer rights.
The faceless assessment procedure under Section 144B stands as a testament to India’s commitment to creating a transparent, efficient, and technology-driven tax administration system that honors honest taxpayers while ensuring robust compliance mechanisms. This revolutionary framework will continue to evolve and adapt to meet the changing needs of a dynamic economy while maintaining its core principles of fairness, transparency, and efficiency.
References
[1] Taxation and Other Laws (Relaxation and Amendment of Certain Provisions) Act, 2020. Available at: https://indiankanoon.org/doc/162681763/
[2] Clear Tax. (2025). Faceless Assessment Scheme Under Section 144B of Income Tax Act. Available at: https://cleartax.in/s/e-assessment-scheme-2019
[3] Income Tax Act, 1961, Section 144B. Available at: https://www.taxtmi.com/acts?id=3299
[4] TaxGuru. (2021). CBDT set-up National Faceless Assessment Centre (NaFAC). Available at: https://taxguru.in/income-tax/cbdt-set-up-national-faceless-assessment-centre-nafac.html
[5] TaxGuru. (2020). CBDT notifies 4195 Income Tax Authorities for Faceless Assessment. Available at: https://taxguru.in/income-tax/cbdt-notifies-4195-income-tax-authorities-faceless-assessment.html
[6] TaxGuru. (2021). CBDT notifies one more exception to Faceless Assessment Scheme. Available at: https://taxguru.in/income-tax/cbdt-notifies-exception-faceless-assessment-scheme.html
[7] India Filings. (2024). Section 144B of Income Tax Act: Faceless Assessment. Available at: https://www.indiafilings.com/learn/section-144b-of-income-tax-act/
[8] TaxGuru. (2022). SOP for Faceless Income Tax Assessment under Section 144B. Available at: https://taxguru.in/income-tax/sop-faceless-income-tax-assessment-section-144b.html
[9] Live Law. (2022). Gujarat High Court Quashes Assessment Order Of Income Tax Worth Rs. 101 Crores For Not Following Natural Justice. Available at: https://www.livelaw.in/news-updates/gujarat-high-court-quashes-assessment-order-income-tax-not-following-natural-justice-217729
[10] Live Law. (2023). Gujarat High Court Quashes Faceless Assessment Order For Lack Of Proper Opportunity Of Hearing. Available at: https://www.livelaw.in/high-court/gujarat-high-court/gujarat-high-court-faceless-assessment-order-opportunity-hearing-235721
Published and Authorized by Dhrutika Barad
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp